Semaglutide
What It Is Used For
- Wegovy is prescribed for chronic weight management in patients with obesity or overweight (BMI criteria apply).
- It is prescribed in conjunction with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
- It is especially helpful for patients with weight-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or dyslipidemia.
How It Works
- Wegovy is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, like Ozempic (approved for diabetes management), designed to regulate appetite and energy balance.
- It mimics a natural hormone that targets areas of the brain responsible for appetite control, helping reduce hunger and calorie intake.
- It also slows stomach emptying, which promotes a feeling of fullness after eating.
How It’s Taken
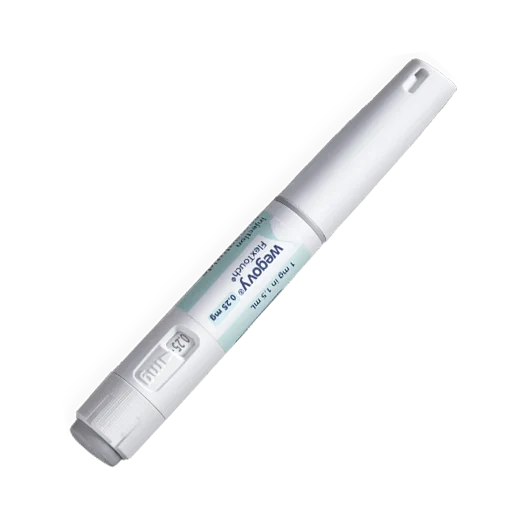
- Wegovy is a once-weekly injectable medication.
- It is injected subcutaneously (under the skin) in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm, at the same time each week.
- Dosing starts at a lower level, 0.25 mg, and is gradually increased over 16-20 weeks to the maintenance dose of 2.4 mg to minimize side effects.
Potential Side Effects
- Common side effects: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, stomach pain, and fatigue. These often improve with continued use.
- Serious side effects: Risk of pancreatitis, gallbladder issues (e.g., gallstones), and rare thyroid tumors.
- Hypoglycemia: While uncommon in non-diabetic patients, low blood sugar may occur, especially if combined with other glucose-lowering drugs.
- Report severe symptoms like persistent nausea, severe abdominal pain, or difficulty swallowing to your healthcare provider.
Precautions and Lifestyle Tips
- Medical history: Disclose any history of thyroid cancer, pancreatitis, gallstones, or kidney disease to your doctor.
- Lifestyle integration: Wegovy works best when combined with a healthy, calorie-controlled diet and regular exercise.
- Missed doses: If you miss a dose and it’s been less than 5 days, take it as soon as possible. If more than 5 days have passed, skip the missed dose and continue with your usual schedule.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to track progress and monitor for side effects.
- Alcohol and interactions: Inform your doctor about alcohol use and all other medications or supplements you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
Liraglutide
What It’s Used For
- Saxenda is prescribed for chronic weight management in patients with obesity or overweight (BMI criteria apply).
- It is used alongside a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
- It may also be recommended for patients with weight-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol.
How It Works
- Saxenda is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, similar to Ozempic (approved for diabetes management), but specifically approved for weight management.
- It helps regulate appetite by acting on brain receptors that control hunger, leading to reduced calorie intake.
- It also slows stomach emptying, helping patients feel full for longer.
How It’s Taken
- Saxenda is a daily subcutaneous injection, administered at the same time each day.
- The injection is given in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm.
- Dosing starts low and is gradually, 0.6 mg, and increased over several weeks to the target dose (3.0 mg daily) to minimize side effects.
Potential Side Effects
- Common side effects: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, headache, and stomach discomfort. These typically improve as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Serious side effects: Risk of pancreatitis, gallbladder problems (e.g., gallstones), thyroid tumors (rare), and kidney issues.
- Low blood sugar: This is more likely in people using Saxenda with other diabetes medications.
- Contact your healthcare provider if you experience severe side effects like abdominal pain, swelling in the neck, or symptoms of dehydration.
Precautions and Lifestyle Tips
- Medical history: Inform your doctor if you have a personal or family history of thyroid cancer, pancreatitis, or gallbladder issues.
- Lifestyle changes: Saxenda is most effective when paired with a healthy diet and regular physical activity.
- Missed doses: If a dose is missed, resume the usual schedule. Do not double doses.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with your doctor are essential to assess progress, adjust dosage, and monitor for side effects.
- Drug interactions: Inform your doctor about any other medications, supplements, or herbs you’re taking to avoid potential interactions.
Tirzepatide
What It Is Used For
- Weight Management: Zepbound is an injectable prescription medicine that may help adults with obesity, or some adults with overweight who also have weight-related medical problems, to lose excess body weight and keep the weight off. It should be used with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): Zepbound has received FDA approval for the treatment of moderate-to-severe OSA in adults with obesity. In clinical studies, patients using Zepbound showed significant improvements in OSA symptoms.
How It Works
- Dual Hormone Action: Zepbound is a dual-acting drug that targets both GLP-1 and GIP receptors. By mimicking these hormones, it helps regulate appetite and food intake, leading to reduced calorie consumption.
- Slows Digestion: It slows the movement of food through the stomach, promoting a feeling of fullness after meals and reducing overall appetite.
How It’s Taken
- Administration: Zepbound is administered as a subcutaneous injection once a week. It comes in three doses: 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg. Your healthcare provider will guide you on the appropriate dosing schedule.
- Injection Sites: Common injection sites include the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. It's important to rotate injection sites with each dose to reduce the risk of skin irritation.
Potential Side Effects
- Common Side Effects: Patients may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, and fatigue. These side effects often diminish as your body adjusts to the medication.
- Serious Side Effects: There is a potential risk of thyroid tumors, including cancer. Seek immediate medical attention if you notice symptoms such as a lump or swelling in your neck, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, or shortness of breath.
Precautions and Lifestyle Tips
- Medical History: Inform your healthcare provider if you have a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2), as Zepbound is contraindicated in these conditions.
- Lifestyle Integration: For optimal results, use Zepbound in conjunction with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity. Your healthcare provider can offer guidance on appropriate lifestyle changes.
- Missed Doses: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as possible within 4 days (96 hours) after the missed dose. If more than 4 days have passed, skip the missed dose and take your next dose on the regularly scheduled day. Do not take two doses of Zepbound within 3 days (72 hours) of each other.
Lisdexamfetamine
What It Is Used For
- Lisdexamfetamine is a prescription medication used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in adults and children aged 6 and older BUT it may also be prescribed for binge eating disorder (BED) in adults.
How It Works
- Lisdexamfetamine is a prodrug, meaning it is inactive until your body metabolizes it into dextroamphetamine.
- It affects brain chemicals to help improve focus, attention, and impulse control in people with ADHD and binge eating
How It’s Taken
- Take Lisdexamfetamine exactly as prescribed, typically once daily in the morning.
- It can be taken with or without food.
- Avoid taking it in the afternoon or evening to prevent insomnia.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects:- Decreased appetite
- Dry mouth
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
- Irritability or mood changes
- Increased heart rate or blood pressure
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Severe mood swings or suicidal thoughts
- Circulation issues (e.g., numbness or discoloration of fingers/toes)
Precautions and Lifestyle Tips
- Dependency risk: Lisdexamfetamine is a controlled substance with potential for abuse or dependence. Take only as directed.
- Health conditions: Inform your doctor if you have heart issues, high blood pressure, mental health conditions, or a history of substance abuse.
- Interactions: Avoid mixing with alcohol or certain medications (e.g., MAO inhibitors).
Contrave
What It Is Used For
- Contrave is a prescription medication for weight management in adults with obesity or overweight who have at least one weight-related condition, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol.
- It should be used as part of a comprehensive program that includes a reduced-calorie diet and regular physical activity.
How It Works
- Contrave is a combination of two medications:
- Naltrexone: Typically used for alcohol and opioid dependence, it may help reduce food cravings.
- Bupropion: Often prescribed for depression and smoking cessation, it may help reduce appetite.
- Together, they act on areas of the brain that control hunger and reward, helping to reduce cravings and overeating.
How It’s Taken
- Contrave is an oral medication taken in tablet form.
- Dosing is gradually increased over four weeks to minimize side effects. The usual target dose is two tablets twice daily (morning and evening).
- Tablets should be swallowed whole and not crushed, chewed, or divided.
- Avoid taking Contrave with high-fat meals, as this can increase the risk of side effects.
Potential Side Effects
- Common side effects: Nausea, constipation, headache, dizziness, dry mouth, and trouble sleeping (insomnia).
- Serious side effects: Increased risk of seizures (especially in people with a history of seizures), elevated blood pressure, and liver problems.
- Mental health concerns: Bupropion may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors, particularly in younger patients. Notify your doctor if you notice mood changes, depression, or anxiety.
Precautions and Lifestyle Tips
- Medical history: Inform your doctor if you have a history of seizures, eating disorders, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or opioid use, as Contrave may not be suitable for you.
- Avoid opioids: Do not take Contrave if you are using opioid medications, as naltrexone can block their effects and cause withdrawal symptoms.
- Alcohol and drug interactions: Limit alcohol use and discuss all medications or supplements you are taking with your doctor to prevent interactions.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-ups are necessary to monitor weight loss progress, blood pressure, and any side effects.
- Lifestyle changes: Combining Contrave with diet, exercise, and behavioral modifications improves the likelihood of success.